
In this article we will learn how we can create an AWS EC2 instance by using terraform.
What is terraform?
Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code (IaC) tool developed by HashiCorp. It allows you to define, create, and manage infrastructure resources in a declarative way, using a high-level configuration language. With Terraform, you can easily provision, update, and delete infrastructure resources, such as virtual machines, databases, load balancers, and more, across multiple cloud providers or on-premises data centers.
Terraform is designed to be cloud-agnostic, meaning that it can be used to manage infrastructure resources across different cloud providers, such as AWS, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, and others. This makes it a powerful tool for DevOps teams who need to manage complex infrastructure across multiple cloud platforms.
In this blog I'll be more focused with AWS
What is EC2 instance?
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a web service that provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. EC2 instances are virtual servers provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that can be launched in a matter of minutes, and are available in a wide variety of configurations, including different instance types, operating systems, and storage options.
Each EC2 instance runs on a virtual machine that is hosted on physical hardware within an AWS data center. You can launch EC2 instances from pre-configured Amazon Machine Images (AMIs), which are essentially templates that contain a specific operating system and set of software applications. You can also create your own custom AMIs to use as the basis for your EC2 instances.
EC2 instances are highly scalable and flexible, and can be used for a wide variety of applications, such as hosting web applications, running databases, performing data processing tasks, and more.
Installing AWS CLI and configuring aws
To get started, we will have to configure aws profile. For this make sure you have aws cli installed. AWS CLI install and update instructions.
MacOS (using brew):
$ brew install awscli
Linux x86 (64-bit):
Run the command one by one
$ curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
$ unzip awscliv2.zip
$ sudo ./aws/install
Linux ARM:
$ curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-aarch64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
$ unzip awscliv2.zip
$ sudo ./aws/install
Once, the AWS CLI is installed let us now configure aws. For this run the below command and provide the needful
$ aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [None]: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
Default region name [None]: us-west-1
Default output format [None]: json
To make sure we have successfuly donfigured AWS run and see the output
$ aws configure list
Name Value Type Location
---- ----- ---- --------
profile local env ['AWS_PROFILE', 'AWS_DEFAULT_PROFILE']
access_key ****************4424 config-file
secret_key ****************RnTe config-file
region eu-west-1 config-file ~/.aws/config
Installing Terraform
As we have learned about terraform let us now install terraform. Install Terraform to finally create an AWS EC2 instance.
MacOS (using brew):
Follow the below commands to install terraform.
$ brew install hashicorp/tap/terraform
Linux:
Follow the below commands to install terraform.
$ curl https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/1.0.5/terraform_1.0.5_linux_amd64.zip --output terraform_1.0.5_linux_amd64.zip
$ unzip terraform_1.0.5_linux_amd64.zip
$ sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin/terraform
To make sure terraform is successfully installed run
terraform --version
Creating an EC2 instance using terraform
In order to create an EC2 instance using terraform we will have to use the aws profile which we created earlier. To use the AWS profile run
$ export AWS_PROFILE=local
The name of my aws profile is local
Now, let us create a new file create-ec2.tf. .tf file is a terraform file extention. Copy the following code to the file.
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1"
}
resource "tls_private_key" "private_key" {
algorithm = "RSA"
rsa_bits = 4096
}
resource "aws_key_pair" "generated_key" {
key_name = "ride-share-key"
public_key = tls_private_key.private_key.public_key_openssh
}
resource "aws_security_group" "security_group" {
name = "ride-sharing-sg"
description = "Allow SSH inbound traffic"
ingress {
from_port = 22
to_port = 22
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "ride_share_instance" {
ami = "ami-14c5486b"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
key_name = aws_key_pair.generated_key.key_name
tags = {
Name = "ride-share"
}
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.security_group.id]
}
output "private_key" {
value = tls_private_key.private_key.private_key_pem
sensitive = true
}
In this example, we are using the aws provider to specify that we want to create resources in the AWS cloud, specifically in the us-east-1 region.
Next, we define a resource of type aws_instance, which creates an EC2 instance. We specify the Amazon Machine Image (AMI) and instance type we want to use, as well as a tag to identify the instance.
Also, we have created a key-pair so that we can attach it with the ec2 instance and a security group to allow inbound and outbound access.
We have the script ready, now, it is time to run the script. Run the terraform init command to initialize the Terraform environment. We would then run the terraform apply command to create the EC2 instance.
$ terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Reusing previous version of hashicorp/aws from the dependency lock file
- Using previously-installed hashicorp/aws v4.65.0
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
$ terraform apply
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource
actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
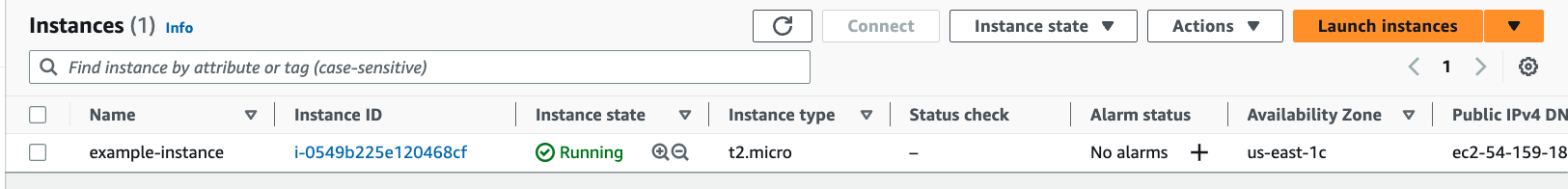
With this we have successfully created an EC2 instance in the AWS Cloud.
Updating the EC2 instance
With Terraform, you can easily modify or delete the resources you've created as well. Let's say you want to modify the aws_instance resource we defined earlier to use a different instance type. You could update the instance_type argument in the configuration file, like this:
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1"
}
resource "tls_private_key" "private_key" {
algorithm = "RSA"
rsa_bits = 4096
}
resource "aws_key_pair" "generated_key" {
key_name = "ride-share-key"
public_key = tls_private_key.private_key.public_key_openssh
}
resource "aws_security_group" "security_group" {
name = "ride-sharing-sg"
description = "Allow SSH inbound traffic"
ingress {
from_port = 22
to_port = 22
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "ride_share_instance" {
ami = "ami-14c5486b"
instance_type = "t3.micro" # CHANGED HERE
key_name = aws_key_pair.generated_key.key_name
tags = {
Name = "ride-share"
}
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.security_group.id]
}
output "private_key" {
value = tls_private_key.private_key.private_key_pem
sensitive = true
}
After saving the updated configuration file, you can run terraform apply again to apply the changes. Terraform will detect that the instance type has changed and prompt you to confirm the changes before proceeding.
$ terraform apply
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource
actions are indicated with the following symbols:
~ update in-place
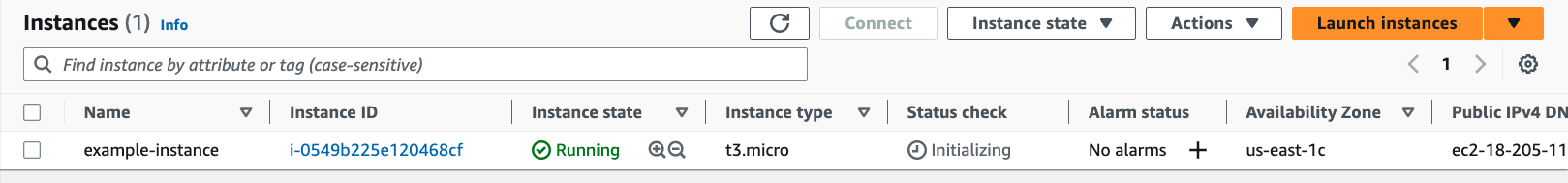
Deleting the EC2 instance
If you want to delete the resources, you can run terraform destroy. This will remove all the resources defined in the Terraform configuration file.
$ terraform destroy
aws_instance.example: Refreshing state... [id=i-0549b225e120468cf]
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource
actions are indicated with the following symbols:
- destroy
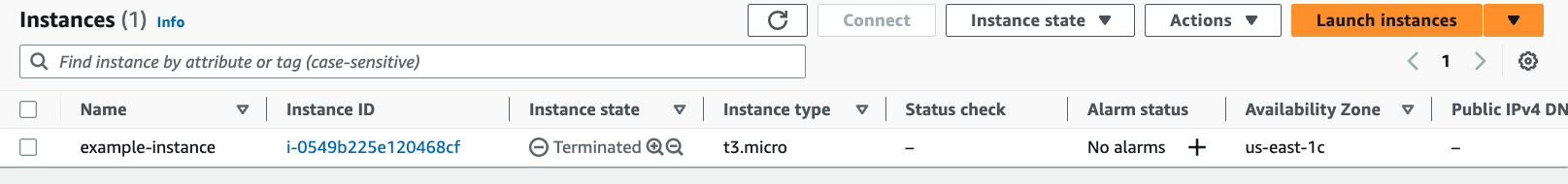
Source Code
https://github.com/Pratap22/terraform/tree/create-ec2
Conclusion
In this blog, we have learned how to create, update and destroy an EC2 instance using terraform.
Learn More
- Exploring the Power of macro_rules! in Rust
- How to Setup Path Aliases in a React Native app with Typescript
- SSH Not Working In MacOS Ventura: How To Fix
Please let me know if there's anything else I can add or if there's any way to improve the post. Also, leave a comment if you have any feedback or suggestions.

Discussions